1. What is Electronic Load Overshoot Phenomenon?
Electronic load overshoot refers to the situation where the current or voltage briefly exceeds the expected stable value during load startup or restart.
Taking a simple example of a power supply charging a capacitor, at the moment the power is connected, since the voltage across the capacitor cannot change abruptly, the capacitor acts as a short circuit, resulting in a large current surge. This current surge is known as current overshoot.
In practical applications, such as in switch-mode power supply circuits, when the load is suddenly connected or the power supply starts up, the output current may rise rapidly and exceed the normal operating current. This is referred to as electronic load current overshoot. Voltage overshoot is similar, where the voltage momentarily exceeds the normal set voltage value. This overshoot phenomenon can potentially damage electronic components and affect the normal operation and lifespan of the circuit.
2. How to Resolve Electronic Load Overshoot?
Enable Soft Start Function: The soft start function of an electronic load can make the loading process smoother. When soft start is enabled, the electronic load will gradually increase the load current according to preset parameters, avoiding sudden current changes that can cause overshoot.This is similar to gradually accelerating a car, avoiding sudden surges of current or voltage, thereby reducing the likelihood of overshoot.
APM's built-in soft start function includes slope settings and other parameter configurations.
(1)Adjust Slope Settings: If the electronic load has slope control functionality, reducing the current or voltage rise slope can slow down the loading process, thereby avoiding overshoot. For example, when testing a power supply, setting the current slope to a smaller value, such as 0.1A/s, means the electronic load's current will increase slowly from 0A at a rate of 0.1A per second. This gives the power supply sufficient time to adjust its internal feedback loop, allowing the output to smoothly adapt to changes in load current.
(2)Other Parameter Settings: On the load settings page, configuring the starting load voltage, unloading voltage, and maintaining the load state can effectively resolve load overshoot issues.
For example, in the APM electronic load series EL200VDC5600W during switch-mode power supply testing, the test conditions are as shown:
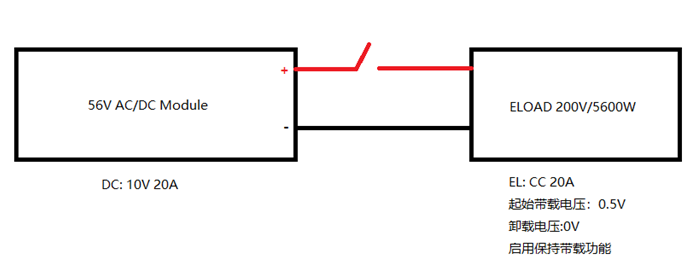
If the customer's operation process is Load OFF >> Load ON >> DC ON, the load may produce the following overshoot waveform:
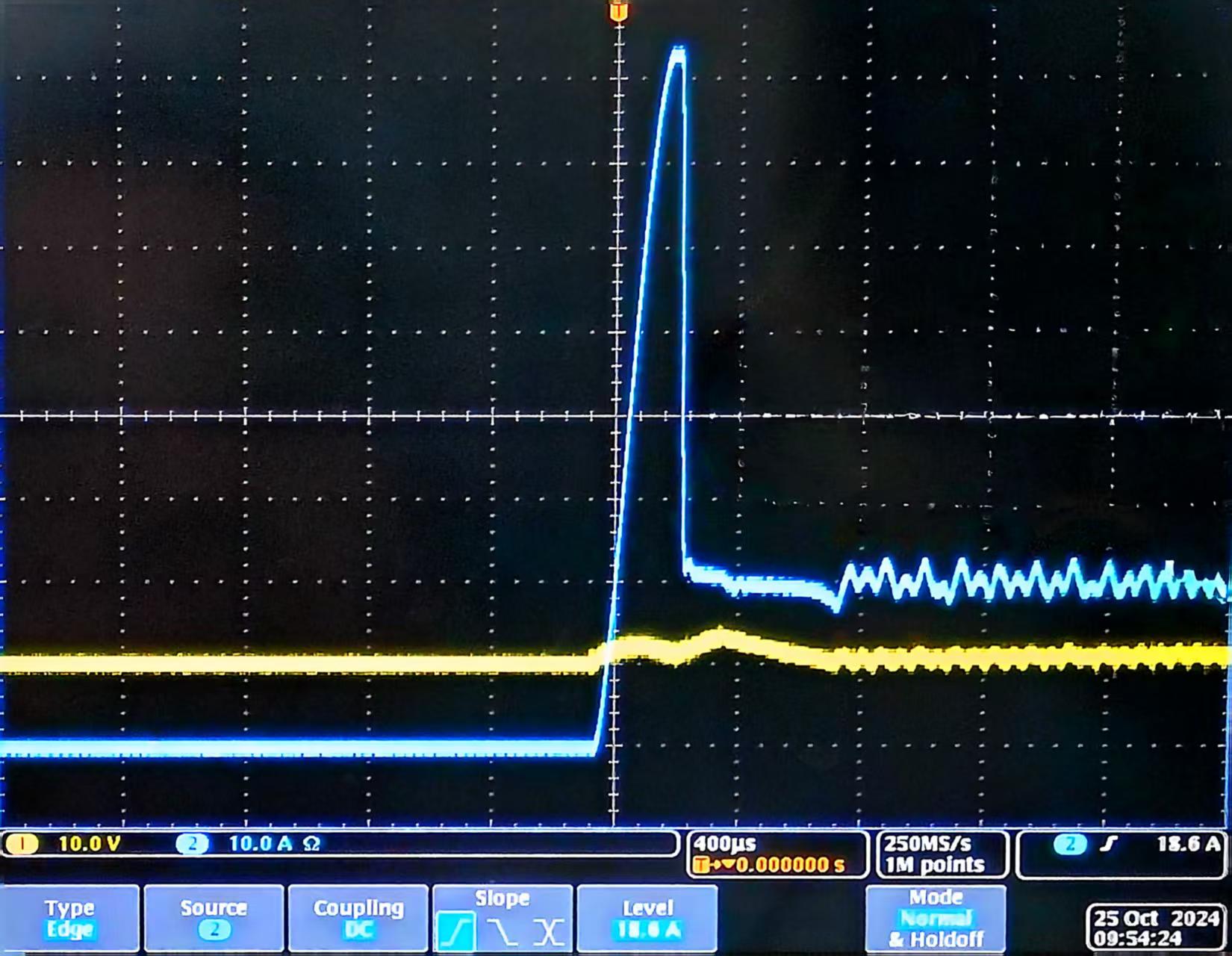
The overshoot occurs because the Von (starting load voltage) is set too low during startup, causing the load voltage to start drawing current when it approaches Von. As a result, the DUT (Device Under Test) output voltage cannot reach the load setting, and the load enters a saturated state (approaching a short circuit), leading to current overshoot. In this case, appropriately increasing the Von setting ensures that the load voltage does not prematurely reach saturation during startup, effectively avoiding overshoot.
As shown below, setting Von=5V results in a current waveform without overshoot, and the machine starts up normally.
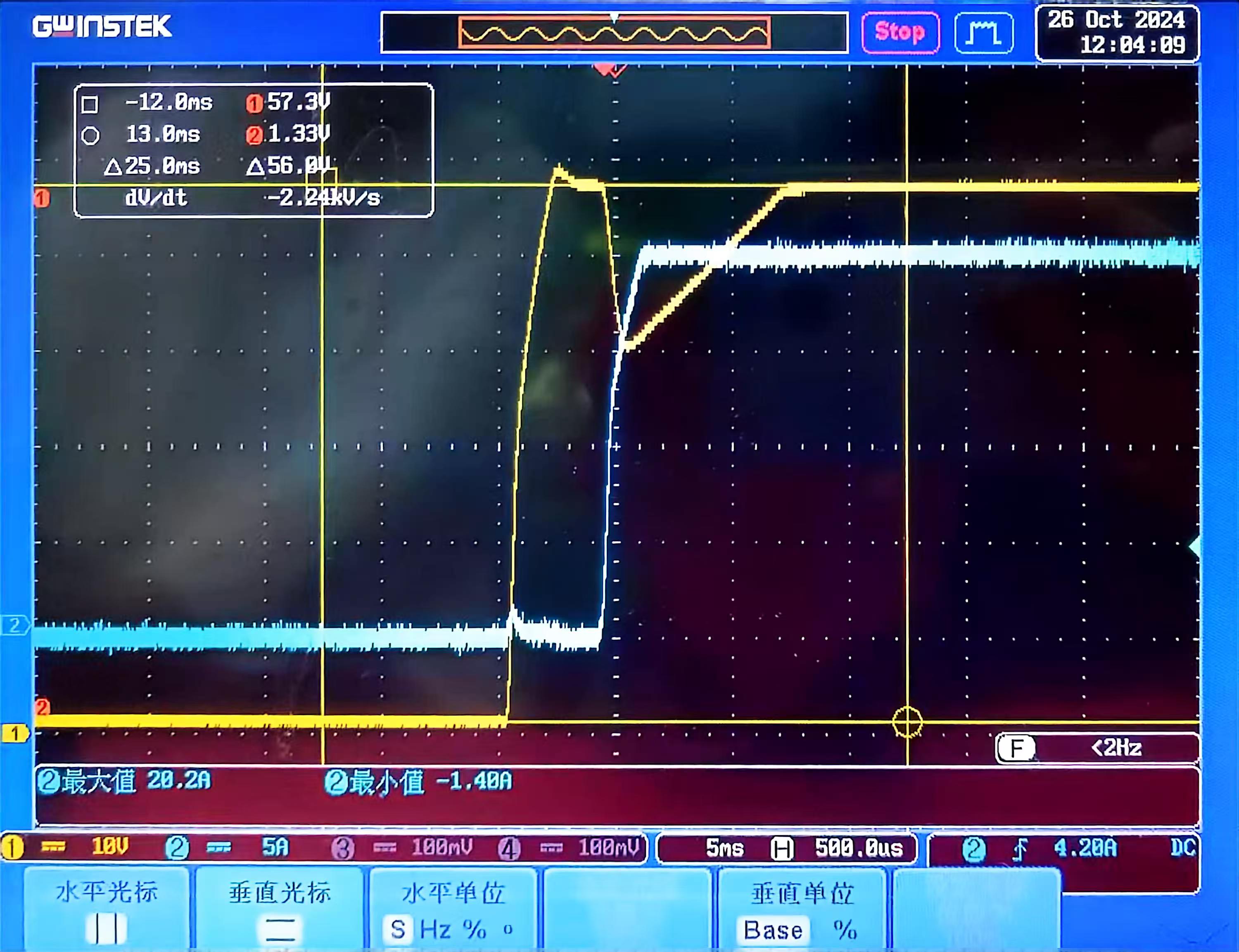
If other conditions remain unchanged and Von is increased (assuming Von=5V), but the customer's operation process is Load OFF >> Load ON >> DC ON >> DC OFF >> DC ON, and overshoot still occurs, the cause of the overshoot is likely due to the Keep Load On=Enable (enabling the keep load function). When the keep load function is enabled, if the DUT stops outputting after normal loading, the load will remain in a current-drawing state. When the DUT restarts, since the load is still in a near-short-circuit state, current overshoot will occur. In this scenario, disabling the keep load function prevents the load from remaining in a current-drawing state after output stops, thereby reducing current overshoot during restart. Alternatively, enabling the keep load function while providing a Voff (unloading voltage) (Voff <= Von) can stop the load when the voltage is too low, preventing current overshoot.
Add Buffer Circuit: Adding a buffer circuit, such as a small inductor in series or a large capacitor in parallel, between the power supply output and the electronic load can effectively suppress overshoot. When the power supply is turned on, the inductor can impede rapid current changes, and the capacitor can absorb instantaneous voltage fluctuations.
In conclusion, a deep understanding of electronic load overshoot phenomena and proactive measures are essential to ensure stable equipment operation and enhance system performance. With ongoing technological advancements, further optimization of electronic load characteristics is expected, reducing the risks associated with overshoot.



